Table of Contents
What Is SEO ROI?
SEO ROI is a calculation that returns the ratio of profit to investment from an SEO campaign. A site will have a positive return on investment if SEO generates more organic revenue or conversions than the overall cost of the campaign. While initially it may take months for SEO to have a positive ROI, the return on investment can compound throughout the years.
Related Content:
To better utilize our SEO ROI calculator, you can use the following steps to determine your input values:
1. Additional Organic Traffic – Yearly
This metric should indicate how much you would like your organic traffic to grow in the next 12 months. The more organic traffic that you receive, the more opportunities you’ll have to convert those sessions into customers. Since the goal of SEO is to improve ranking positions, ideally your site will be generating more organic traffic than it was previously.
It might be a little difficult to determine how much you should expect your organic traffic to grow by. Below are some factors that can better help you set realistic goals for this metric:
1. Size Of Website
When estimating the amount of additional organic traffic for the SEO ROI calculator, it’s important to set realistic goals based on the size of your website. For instance, if your site generates 100,000+ organic sessions a month, a goal of improving organic traffic by 40% may be difficult to hit. Instead, a goal of 10% growth might be more reasonable given the large amount of traffic you’re getting. For smaller sites, larger percentage increases might be more realistic.
2. Search Volume Of Target Keywords
As well, the search volume of your target keywords also plays a crucial role in determining your target organic traffic increase. Your industry and product will dictate the amount of search opportunity. For example, a company selling “watches” might target keywords with much larger volumes than a niche SaaS product. The total volume of your core keywords can give you a better indication of what your aggregate search potential looks like.
3. Existing Rankings
If you’re using your aggregate search volume to estimate organic traffic increases, you’ll want to be sure to pair that data with existing rankings. For instance, if you’re ranking
Keyword Volume: 10,000
Current Rank: 8
Goal Rank: 5
You could then estimate the value of this rank change by using a standard click through rate model:
Position 1: 26.4%
Position 2: 15.2%
Position 3: 11.2%
Position 4: 8.4%
Position 5: 5.8%
Position 6: 4%
Position 7: 3%
Position 8: 2.2%
Position 9: 1.7%
Position 10: 1.3%
*Data from AdvancedWebRanking
You could apply the click through rate model to estimate the change in monthly search volume:
(10,000*.058)-(10000*.022)
In the above example the change in ranking position would result in 360 additional organic sessions.
2. Average Conversion Value
As well, when determining the return on investment of SEO, it’s important to understand how much your average conversion value is. While obviously this is going to vary depending on the product or service that you offer, determining some estimates here can be beneficial when evaluating the returns you might get from SEO.
Ecommerce Average Conversion Value
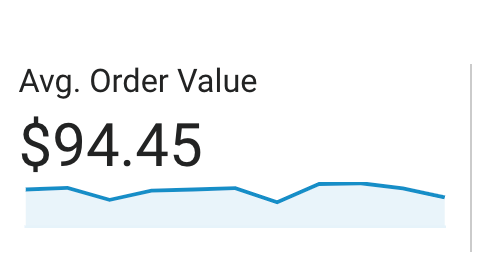
If you’re an eCommerce store, this can be pretty straightforward. If you have eCommerce tracking set up in Google Analytics you can find your Average Order Value by navigating to Conversions > Ecommerce > Overview. This will show you your site’s average order value.
Non-Ecomerce Average Conversion Value
If you’re not an eCommerce site, then you’ll need to determine your customer lifetime value and lead-to-customer conversion rate. This will help you set a “Goal Value” in Google Analytics.
For instance, let’s use an example where you have determined the following data points about your customers:
Customer Lifetime Value = $10,000
Lead Conversion Rate = 20%
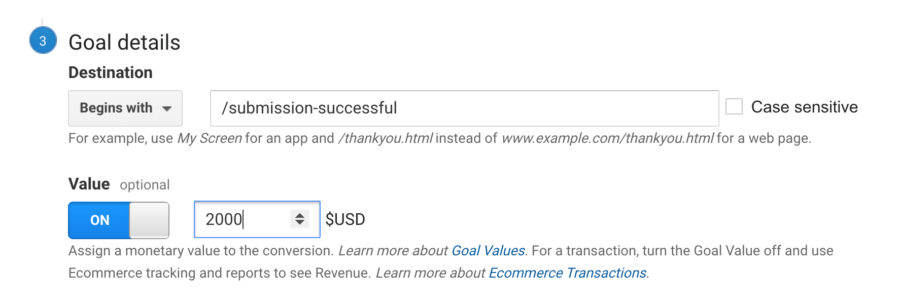
Since you know that that you will convert 20% of your leads into customers and each customer is worth $10,000, this means that each lead will be worth $2,000 for that particular goal. With this information, you can actually add this information to your Google Analytics view. This will give you revenue estimates for non-ecommerce conversions.
To add this information into Google Analytics, simply do the following:
- Select the gear icon to access your “Admin” settings
- Navigate to “Goals”
- Select the goal you want to assign a value to
- Click “Goal Details”
- Ensure that “Value” is turned on and add your goal value
3. Average Conversion Rate
Now that you have identified the average conversion value of your customers, the next thing you’ll need to determine is the average conversion rate. Conversion rate tells you what percentage of sessions will convert into sales or leads.
Fortunately, for both eCommerce and non-eCommerce sites, this is easy to find in Google Analytics:
- Ecommerce stores: This can be found in Conversions > Ecommerce > Overview. This report should show you an “Ecommerce Conversion Rate”
- Non Ecommerce sites: This is in Conversions > Goals > Overview > Goal Option. Simply choose your primary conversion goal from the list in “Goal Option” and you should be able to view your goal conversion rate
Using these conversion rates, you might be able to get a better sense of how many users are likely to convert with traffic improvements.
Traffic Quality
Of course, understand that conversion rate can be impacted by the quality of your traffic. If your SEO campaign is targeting highly qualified terms, than you should see your conversion rate remain stable or even improve. However, if you’re targeting qualified or higher funnel terms, this might result in your conversion rate lowering. The classic example is a site generating a large amount of traffic from the blog but seeing a large drop in conversion rate as these users are not looking to convert.
To get a better understanding of conversion rate on high intent pages, you might even consider using a segment in Google Analytics. This segment could only measure traffic to high conversion pages such as landing or product/category pages. This might give you a more accurate idea of conversion rates on lower funnel pages.
4. SEO Campaign Cost – Yearly
This will be the yearly cost of your SEO campaign. If you’re on a monthly retainer, simply multiply your monthly expenses by 12 to get the total cost of your SEO campaign for the year. This is the value that should be added to the last field of the SEO ROI calculator.
[roicalculator heading=”SEO ROI Calculator”][/roicalculator]
You can use our SEO ROI calculator to better estimate the value of SEO for your website.
To use the SEO ROI calculator, you can input how much additional organic traffic you would like to receive to your website. Next, input how much a website conversion is worth to your business and the average conversion rate of your site. The SEO ROI calculator will then return a return on investment value comparing the additional revenue brought in from organic to your yearly SEO costs
Search News Straight To Your Inbox
*Required
Join thousands of marketers to get the best search news in under 5 minutes. Get resources, tips and more with The Splash newsletter: